Distributed Model Predictive Control Architectures for Multi-Rotor Micro Aerial Vehicles
Published:
Semster Research student at Distributed Intelligent Systems and Algorithms Laboratory, EPFL since Feb. 2021
Supervisor: Izzet Kagan Erunsal (PhD student) and Prof. Alcherio Martinoli
Overview
The main goal of this project is to compare the effectiveness of different Distributed MPC architectures and a Decentralized MPC scheme in a leader-follower formation control problem. Several communication flaws such as delay, packet dropout and jitter are implemented in the simulation to test the robustness of the controller. The three Distributed MPC structures for multi-robot formation control are following:
Velocity sharing based
Distribute the overall formation control into several sub-MPC problem and each agent obtain the coupled information, i.e. velocity, of its neighbors from communication.
ADMM-based
Rewrite the centralized problem by introducing several slack variables and distribute it by Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM).
PSO-based
Separate the overall control problem into several sub-task, each agent communicates the global best particle to its neighbors and utilize Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) to solve its subtask based on the particle received from neighbors.
For more details, please refer to the report.
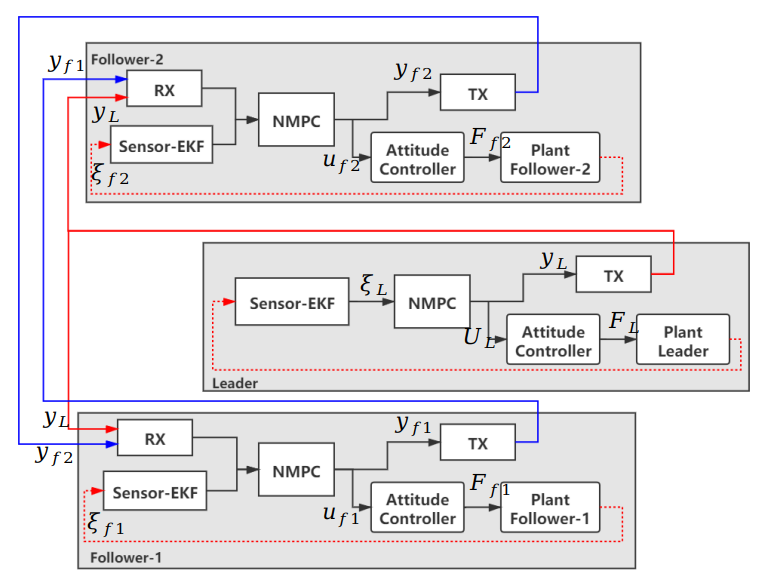
System architecture
Experiments
MATLAB Simulation
The simulation experiments on the three types of Distributed MPC have been carried out in MATLAB 2020b with an Intel i7-8550U processor. The ACADO toolkit with code generation is selected as the solver for the Velocity sharing based. The nonlinear programming in ADMM-based is solved by fmincon in MATLAB. In order to fairly compare the performance, Velocity sharing based is also implemented by fmincon. Finally, PSO-based used particleswarm in MATLAB as the solver.
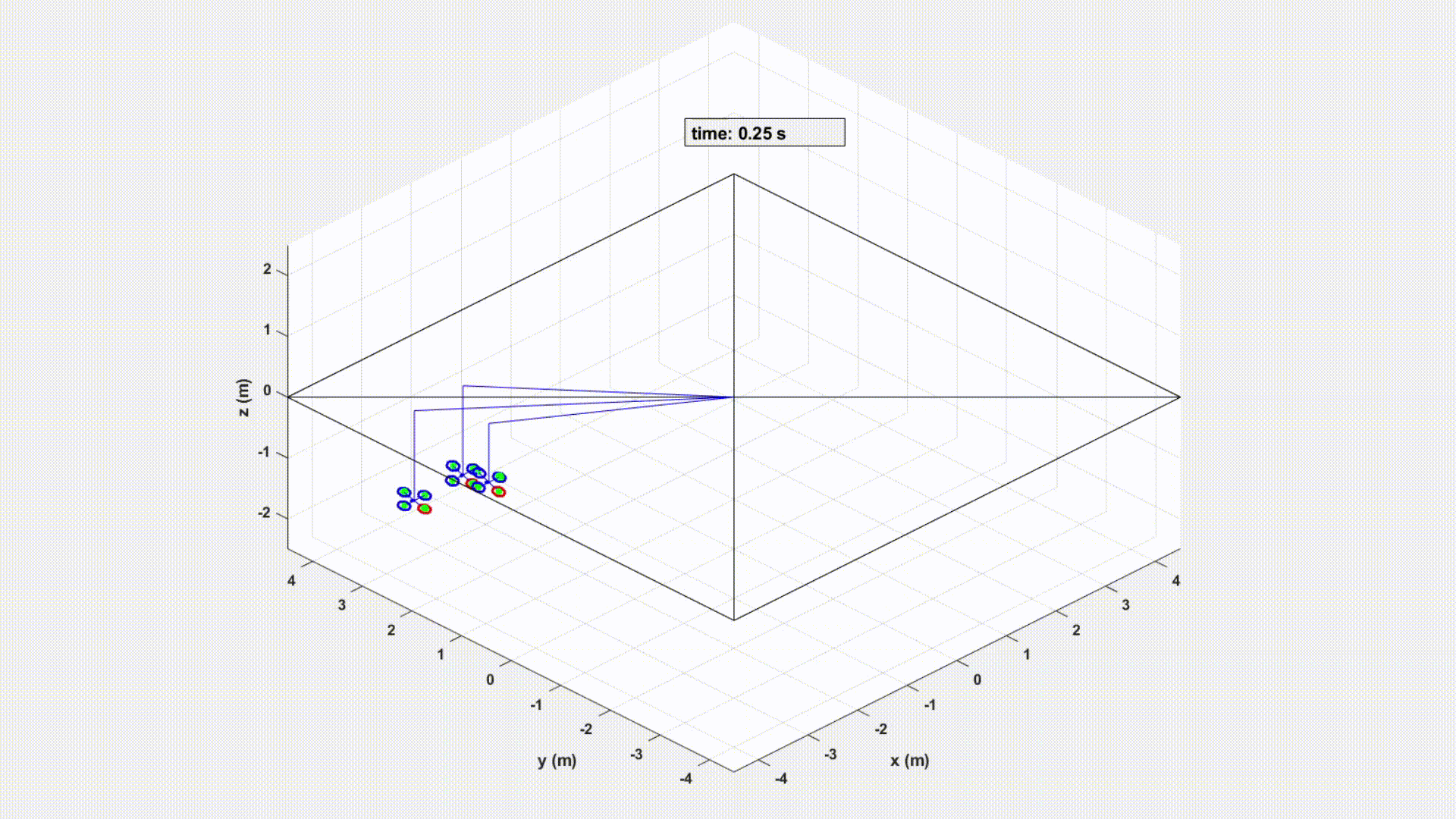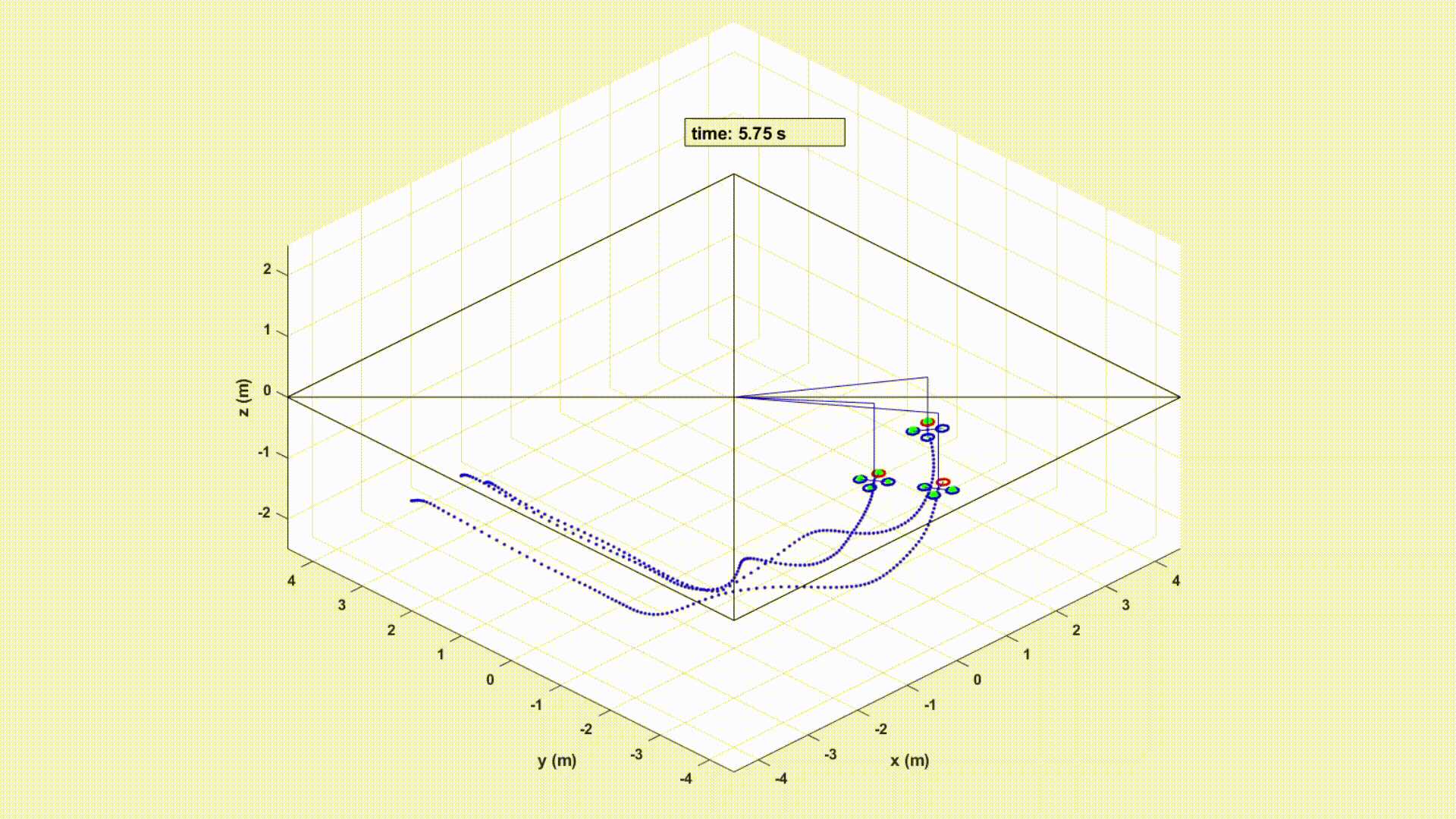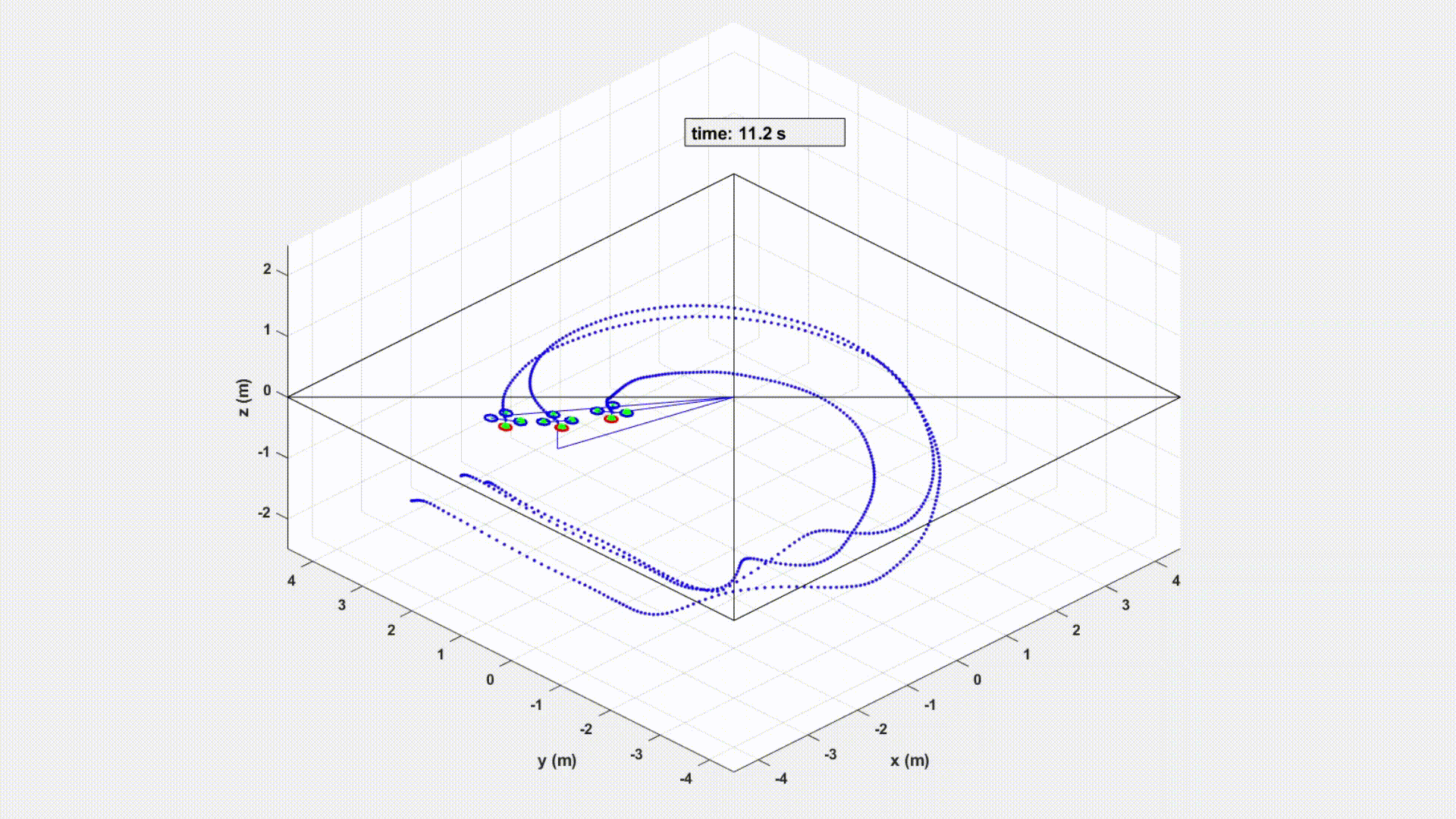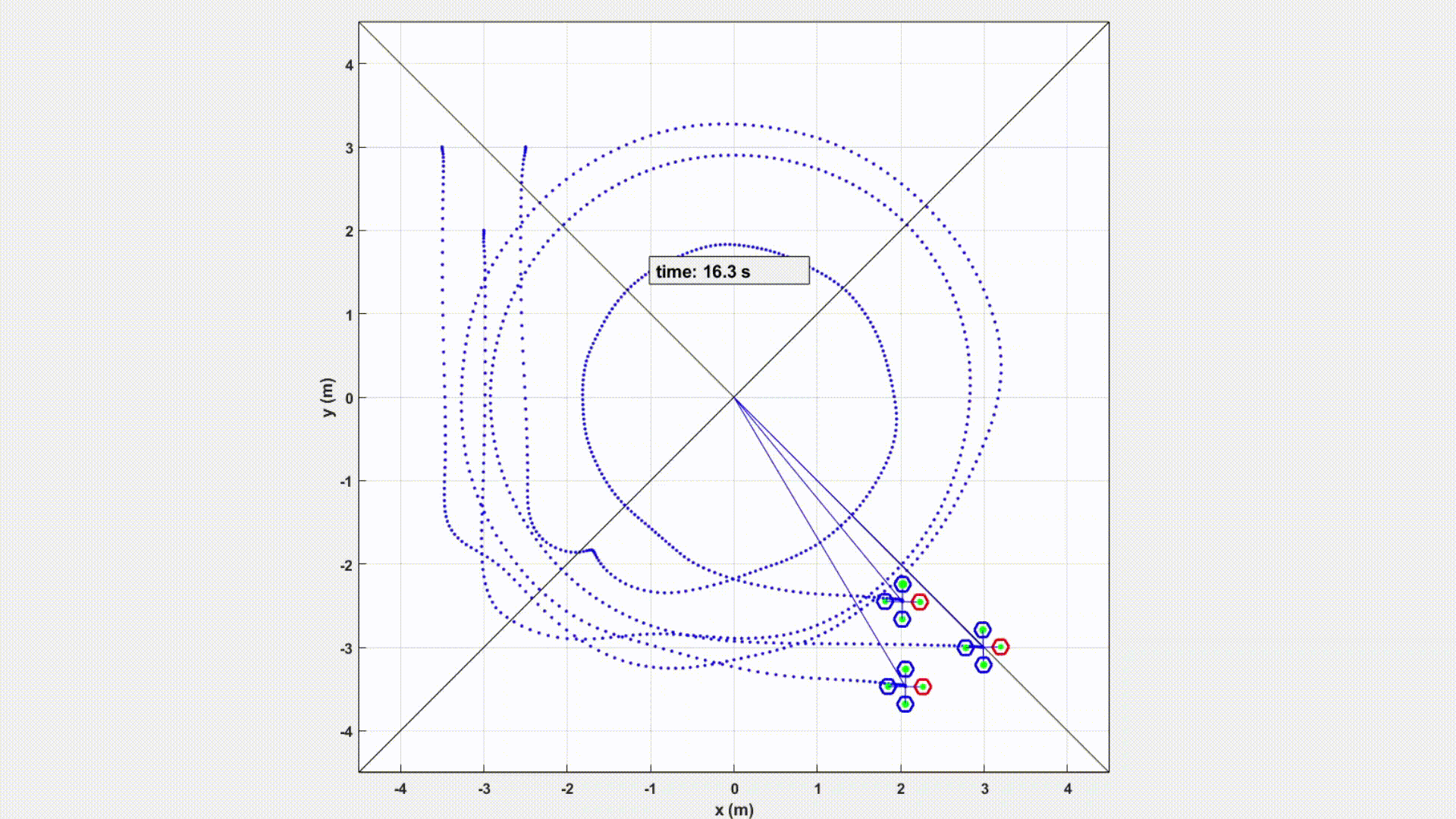
An experiment controlled by Velocity sharing based Distributed MPC in MATLAB
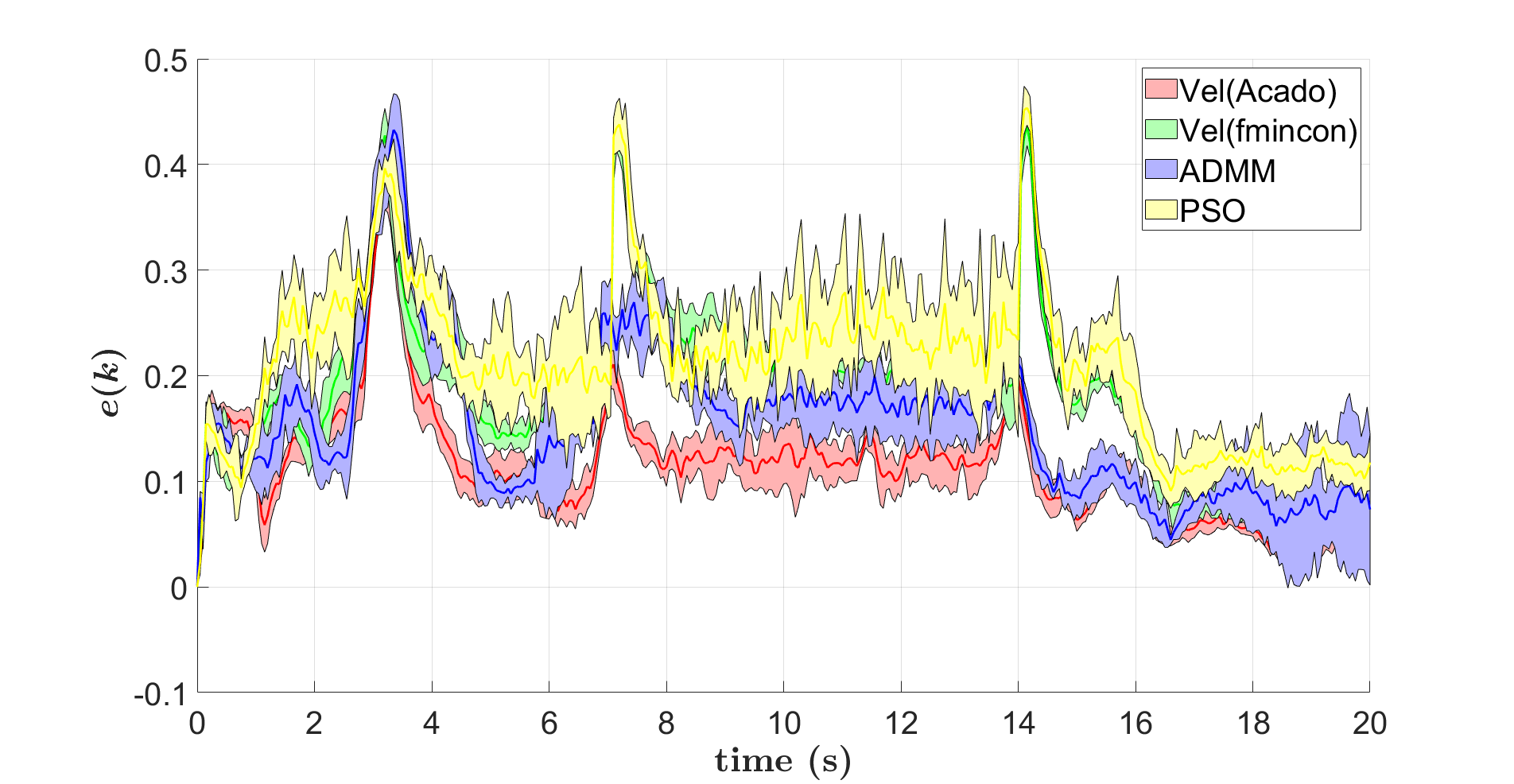 | 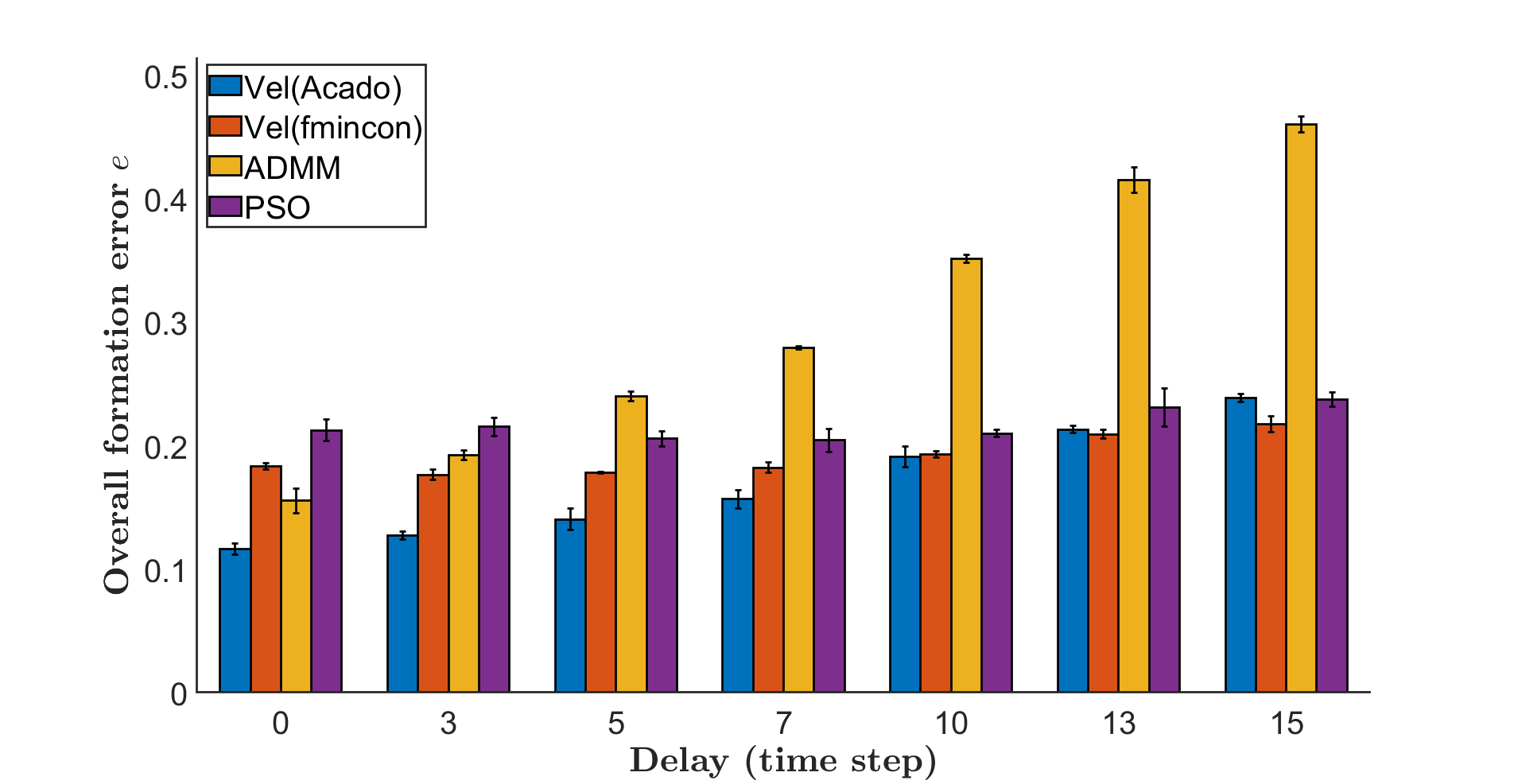 |
Remark
- Velocity sharing based type with Acado has best performance
- ADMM-based has less formation error than Vel-sharing based when using the same solver
- ADMM-based is also promising if it can be implemented in an efficient solver.
- PSO-based Distributed MPC is not suitable for formation control
Webots-ROS Simulation
Webots R2020b and ROS melodic 1.14.11 has been used. In this simulation, Velocity sharing based is compared with a Decentralized MPC controller.
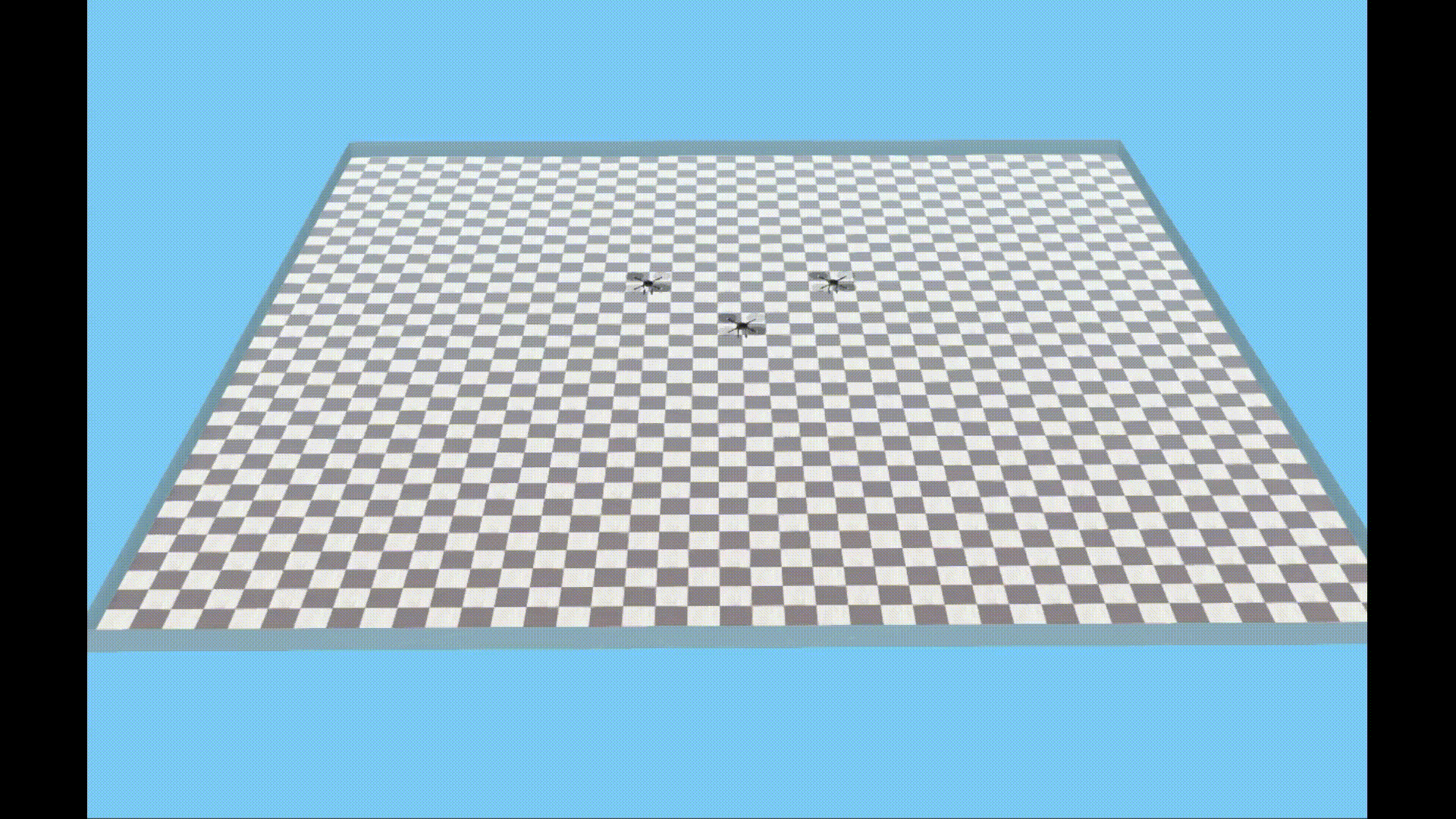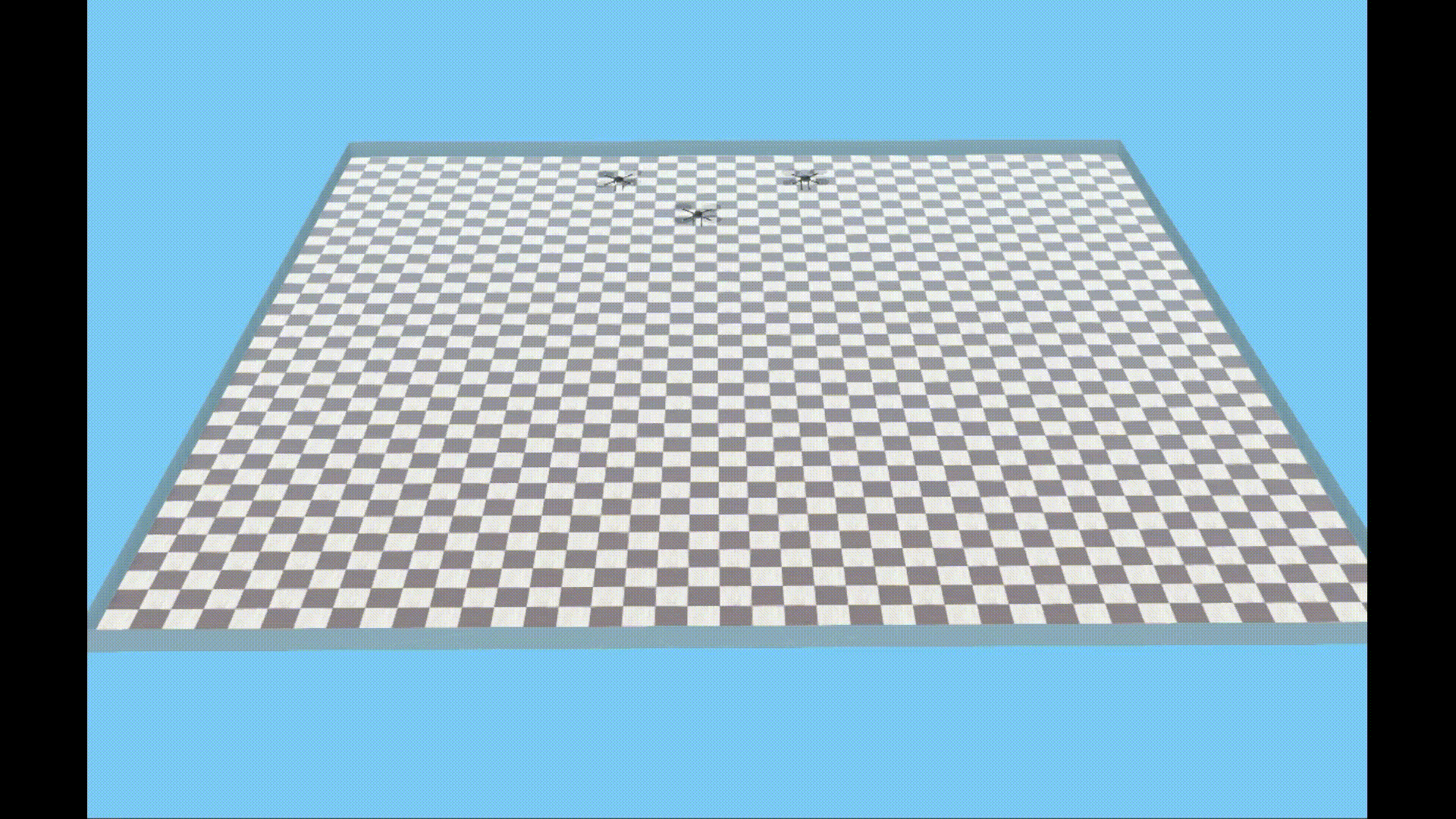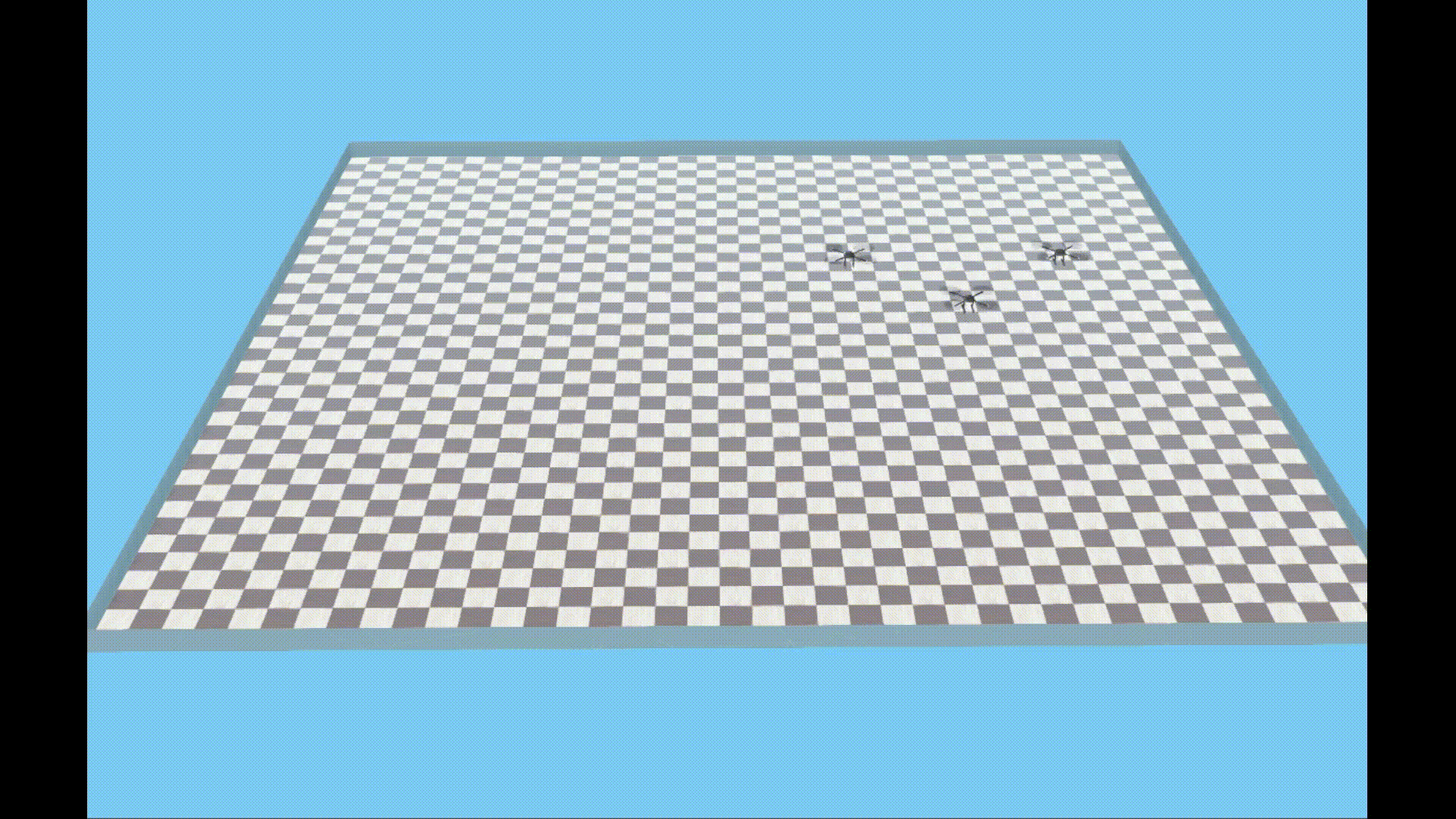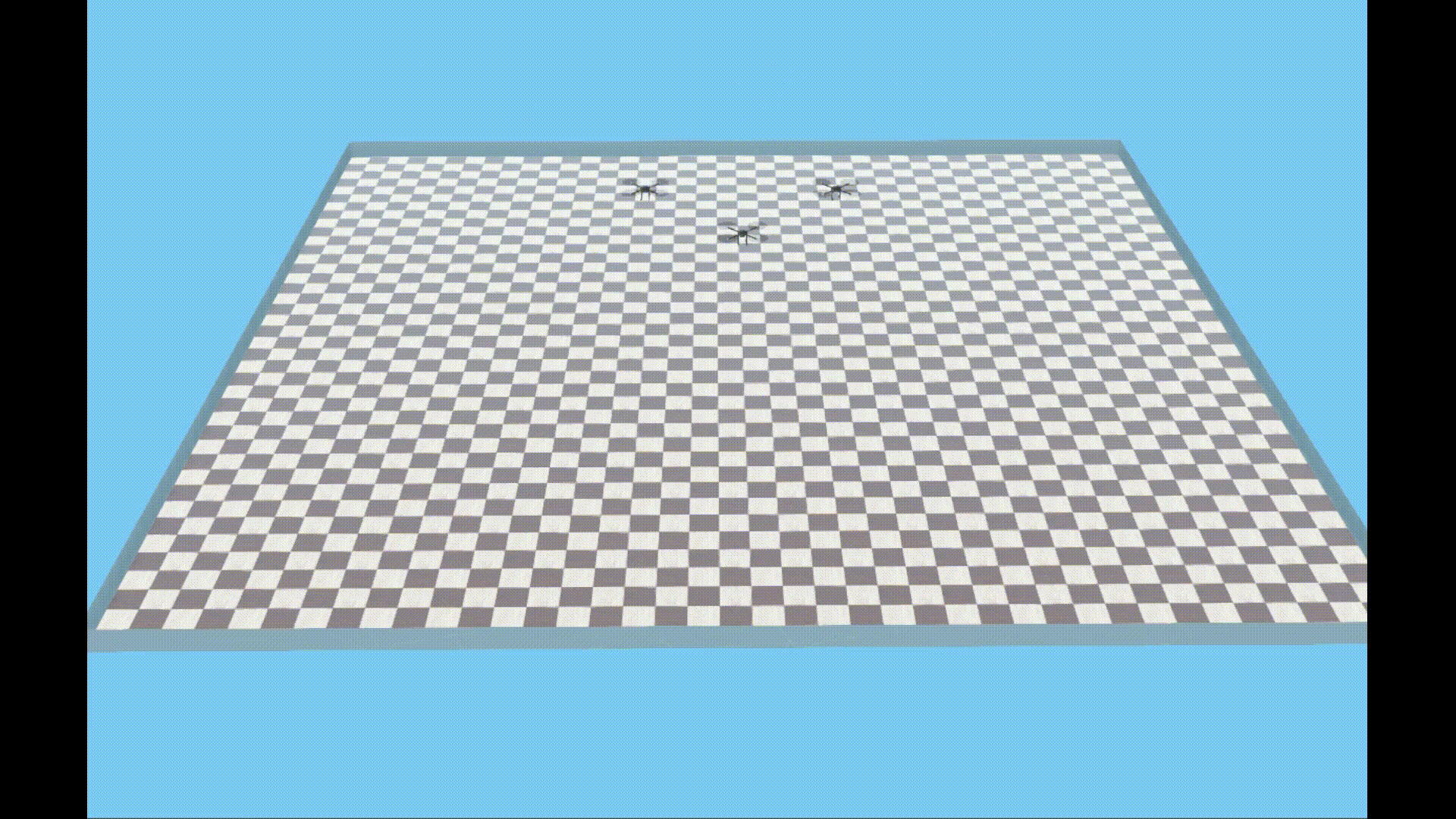
An experiment controlled by Velocity sharing based Distributed MPC in Webots-ROS
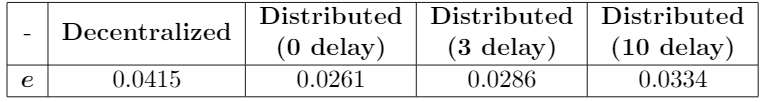
Table of overall average formation error
The simulation results indicated that Velocity sharing based Distributed MPC controller has 37% less formation error than the Decentralized MPC controller. Even with high communication delay, Velocity sharing based Distributed MPC still performs better than the Decentralized one.
For more interesting plots and metrics, please refer to the report.
